FMP
Active vs Passive Investing: Navigating the Investment Landscape
Nov 12, 2023(Last modified: Apr 18, 2024)
Active vs Passive Investing: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of investing, two primary approaches dominate the landscape: active investing and passive investing. While both aim to generate returns for investors, they differ significantly in their philosophies, strategies, and associated risks.
Active Investing: Pursuing Market-Beating Returns
Active investing involves a hands-on approach, where professional fund managers or individual investors actively select and manage a portfolio of securities, aiming to outperform the broader market. Active investors employ various research methods and analytical techniques to identify undervalued stocks or anticipate market trends.
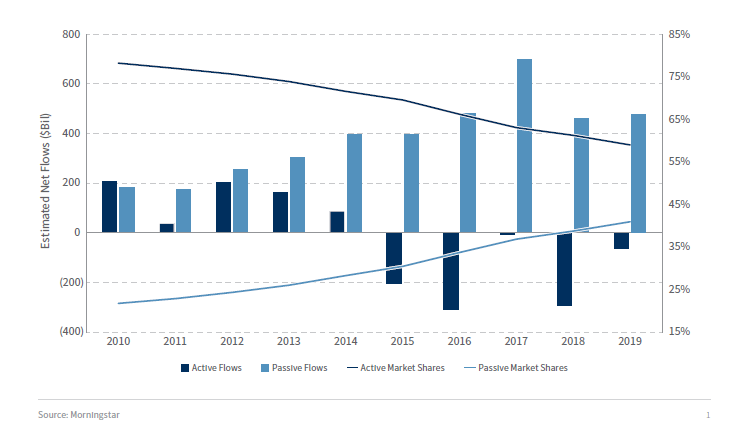
Image:
Key Characteristics of Active Investing:
-
Market Timing: Active investors believe they can outperform the market by identifying undervalued stocks or anticipating market movements.
-
Stock Picking: Active investors actively select individual stocks based on their research and analysis.
-
High Fees: Actively managed funds typically carry higher management fees compared to passive index funds or ETFs.
Passive Investing: Embracing the Buy-and-Hold Strategy
Passive investing, also known as index investing, advocates for a buy-and-hold strategy, focusing on long-term growth rather than short-term market timing. Passive investors typically invest in index funds or ETFs that track broad market indexes, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average.
Key Characteristics of Passive Investing:
-
Market Efficiency: Passive investors believe in the efficient market hypothesis, assuming that stock prices already reflect all available information.
-
Index Tracking: Passive investors seek to replicate the performance of a broad market index, diversifying across a wide range of securities.
-
Low Costs: Passive index funds and ETFs typically carry significantly lower fees compared to actively managed funds.
Comparing Active and Passive Investing: Performance and Statistics
Numerous studies have examined the long-term performance of active vs passive investing strategies. The general consensus suggests that passive investing has historically outperformed active investing over extended periods.
-
S&P 500 Index Performance: Over the past 90 years, the S&P 500 index has yielded an average annual return of around 10%.
-
Active Fund Performance: Studies indicate that only a small percentage of actively managed funds consistently outperform the market over the long term.
-
Cost Impact: The high fees associated with actively managed funds can significantly erode their potential returns compared to low-cost passive index funds or ETFs.
Conclusion
- The choice between active and passive investing depends on an investor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment horizon. Active investing offers the potential for higher returns but comes with the inherent risk of underperforming the market and incurring higher fees. Passive investing provides a more straightforward and cost-effective approach, focusing on long-term growth and minimizing risk through broad diversification.
- For investors seeking long-term wealth accumulation and a disciplined investment approach, passive investing has consistently demonstrated its effectiveness. However, for investors with a higher risk tolerance, extensive market knowledge, and the ability to dedicate significant time to active management, active investing may offer the potential for outsized returns.
- Ultimately, the most suitable investment strategy aligns with an investor's individual circumstances, risk profile, and financial objectives. Carefully evaluating these factors and seeking guidance from financial professionals can help investors make informed decisions that support their long-term financial goals.

Top 5 Defense Stocks to Watch during a Geopolitical Tension
In times of rising geopolitical tension or outright conflict, defense stocks often outperform the broader market as gove...

Circle-Coinbase Partnership in Focus as USDC Drives Revenue Surge
As Circle Internet (NYSE:CRCL) gains attention following its recent public listing, investors are increasingly scrutiniz...

LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton (OTC:LVMUY) Financial Performance Analysis
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton (OTC:LVMUY) is a global leader in luxury goods, offering high-quality products across f...